What is appendectomy?
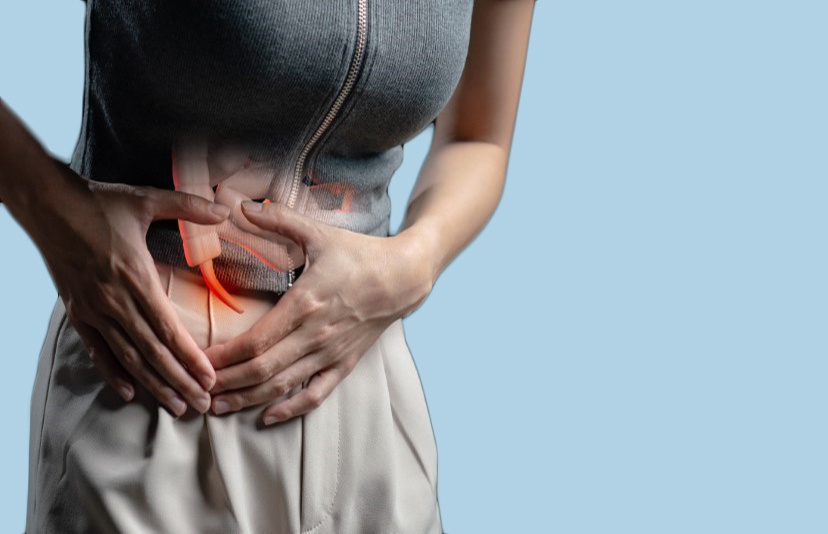
Appendectomy is a surgical procedure that is used for removing an infected appendix. The appendix is a small pouch that connects the large intestine to the stomach, and it is located in the lower right corner of the stomach. When the appendix becomes inflamed, enlarged, and infected, this condition is called appendicitis, and it can be extremely painful to deal with. If left untreated, it can lead to further complications.
In the case of appendicitis, the appendix has to be removed at the earliest to avoid the risk of it bursting. Due to the high level of risk associated with such an event, this condition is considered life-threatening.
Why is an appendectomy required?
If the patient has symptoms of appendicitis; the doctor will suggest an appendectomy procedure to remove the appendix. The symptoms are:
- Pain in the lower abdomen that starts on the right side and progresses to the left.
- Sudden pain in the lower right abdomen that begins around the navel.
- Coughing, walking, or other jarring movements aggravate the pain.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Appetite loss.
- Fever
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating in the abdomen
- Flatulence
There is a significant possibility of the appendix bursting or rupturing if one is suffering from appendicitis, and this might happen within 48 to 72 hours from the onset of symptoms. This condition can also induce peritonitis, a life-threatening infection in the stomach.
The patient must visit the Apollo doctor immediately if the symptoms of appendicitis exist.
What are the types of appendectomy?
The appendix can be removed using two methods- An open appendectomy (most common procedure) or a laparoscopic appendectomy.
- Open appendectomy: For this procedure, the surgeon will make an incision of 2 to 4 inches in the lower right-hand side of the belly or abdomen. Through this incision, the surgeon will gain access to the appendix region and then surgically remove the infected appendix.
- Laparoscopic appendectomy – This type of surgery is a minimally invasive procedure performed without the need for a major incision. During this procedure, one to three small incisions are made around the abdominal region, and a laparoscope (a long, thin tube) is inserted through one of the incisions. The laparoscope consists of a camera at the end. The surgeon uses the feed relayed by the camera to a TV display to see into the abdomen and navigate the laparoscope. On reaching the appendix, the surgeon will use the laparoscope to remove the appendix and stitch up the area to avoid further bleeding. Once the appendix is removed, the surgeon will remove the laparoscope, and the incision(s) will be stitched shut.
What are the risks associated with an appendectomy?
The following are some of the possible risks involved in an appendectomy:
- Bleeding
- Infection at the incision area
- Appendix rupture during surgery, infection, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of the abdomen (peritonitis)
- Bowel blockage
- Organ damage
Other risks that are specific, may exist due to pre-existing conditions or other factors. Before surgery, discuss with the doctor about any concerns.
What are the post-operative care instructions for appendectomy?
At the hospital premises:
After surgery, you will be brought to the recovery room, where the surgical staff will monitor your vital indicators, such as heart rate and respiration. Once the vitals have been deemed stable, the patient will be moved to a standard hospital room.
The patient will also be given pain medication as needed, and this could be from a doctor's prescription or a nurse's recommendation. The patient can also administer it to themselves using a device attached to the IV (intravenous) line if provisioned by the doctor.
A small plastic tube may be inserted into the stomach through the nose. This is utilized to get rid of any stomach fluids or air that the patient may have swallowed. When the bowels start functioning normally, the tube will be removed. The patient won't be allowed to drink or eat until the tube is removed.
The healthcare professional will schedule a follow-up appointment for the patient, and this usually happens in two to three weeks following surgery.
At home
When the patient is at home, make sure the incision site is clean and dry. The doctor will provide specific instructions when it comes to bathing and cleaning the incision site. During a follow-up appointment with the doctor, any stitches or surgical staples that were used for sealing the incision site will be removed. It is vital to keep adhesive strips dry if the patient is using them, as they usually come off within a few days.
The incision area and the abdominal muscles may hurt, especially if the patient stands for long periods. Only take medications that the doctor has prescribed. Aspirin and other pain relievers can make more prone to bleeding.
During recovery, the patient may experience the following symptoms, which necessitate immediate consultation with the doctor:
- Chills or a fever
- Incision site redness, oedema, bleeding, or other discharge
- Increased discomfort in the area of the incision
- Vomiting
- Appetite loss or inability to eat or drink
- Non-stop coughing, breathing problems, or shortness of breath
- Pain, cramping or swelling in the abdomen
- Lack of bowel movement for over two days
- Diarrhea for over three days

Why Choose Apollo Healthcare?
Established By Dr Prathap C Reddy In 1983, Apollo Healthcare Has A Robust Presence Across The Healthcare Ecosystem. From Routine Wellness & Preventive Health Care To Innovative Life-Saving Treatments And Diagnostic Services, Apollo Hospitals Has Touched More Than 120 Million Lives From Over 120 Countries, Offering The Best Clinical Outcomes.
7,000+Healing Hands
4,000+Pharmacies
170+primary care & diagnostic clinics
70+Hospitals






